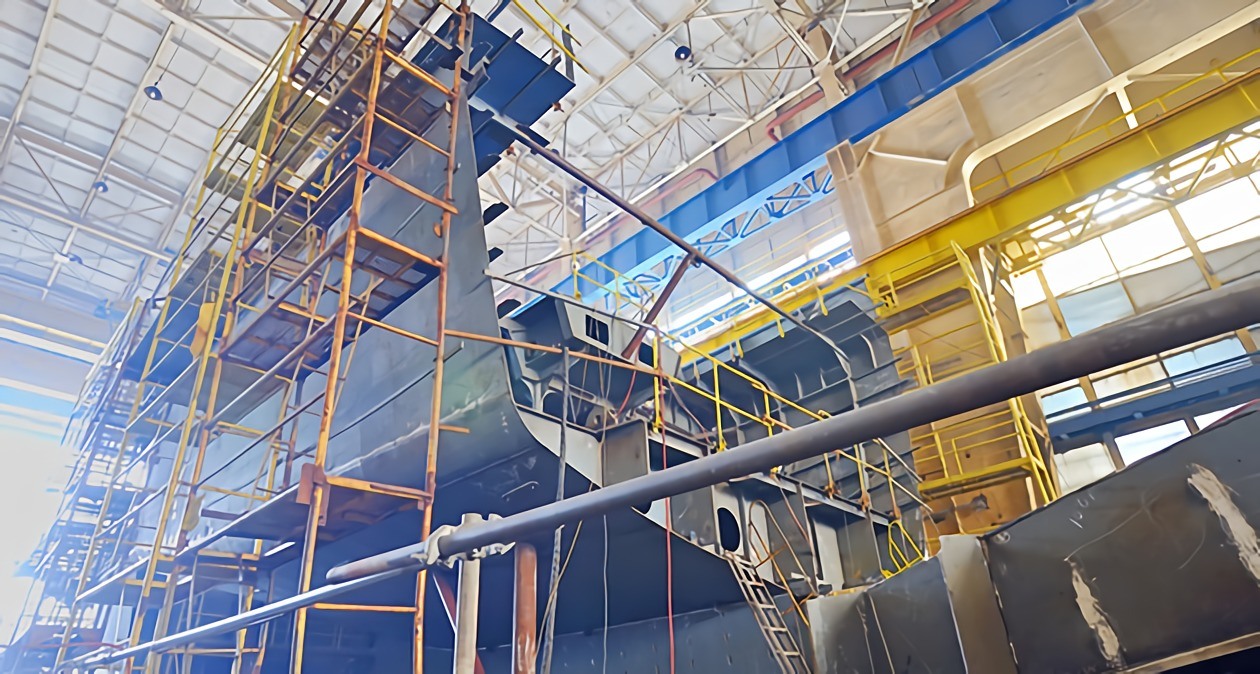
Welders play an important role in the construction and manufacturing industries, fusing the metals found in everything from bridges to automobiles to airplanes. There are more than 100 1 different types of welding processes and selecting the right one depends on the project. However, arc welding—a technique in which metals are welded using heat generated by an electric arc—is the most common type used today. For projects that require the fastening of metal parts, arc stud welding is a quick, highly reliable and efficient option.
What Is Arc Stud Welding?
Arc stud welding is a process by which an electric arc is used to heat a metal fastener, usually referred to as a weld stud, then fusing it under pressure to a metal workpiece. The weld stud is held in place for the welding process by a stud gun.
There are three different techniques employed in arc stud welding:
- Drawn Arc Stud Welding: A process that allows greater penetration of weld depths (1-3mm), produces high-quality welds and is excellent for structural steel engineering, mechanical engineering and shipbuilding.
- Short Arc Stud Welding: Quickest welding technique but can result in porous welds.
- Gas Arc Stud Welding: Provides less penetration depth than the drawn arc technique and is often used in automated and robotic welding processes.
Advantages of Arc Stud Welding
Some advantages to arc stud welding are that it is a fast, easy and relatively inexpensive process:
- Each weld takes less than a second.
- Access to only one side of the surface is needed, resulting in more aesthetically appealing products because the reverse side is not marred.
- Arc stud welding produces strong welds that are vibration-proof and resistant to breaking, loosening or weakening.
- The process eliminates the necessity for punching, drilling, tapping and riveting.
- Training is not time-intensive, and only one worker is necessary to complete a weld, which reduces labor costs.
Applications of Arc Stud Welding
Given the advantages of arc stud welding, it has numerous applications in the construction and manufacturing industries:
Have You Considered a Career in the Skilled Trades?
Fill out the form to recieve a no obligation info packet.
- Automotive and shipbuilding
- Appliance manufacturing
- Aerodynamic industry
- Boilers
- Light or heavy construction
- Preassembled fabrications
Stud Welding Certification
The American Welding Society (AWS) offers a detailed guide for welders with recommendations for the best stud welding practices, including arc stud welding. The AWS offers eight different types of welding certificates a welder can obtain, beginning with certified welder. It is also possible to become certified in a stud welding.
Arc Stud Welding Career Outlook
Arc stud welding is just one of a multitude of techniques available to welders; however, given its numerous advantages and applications, it is definitely one most welders would benefit from mastering. Ultimately, welders with more training and up-to-date skills often enjoy greater job opportunities and higher pay. To learn more about how to enter the dynamic and diverse field of welding, contact Tulsa Welding School today. The school offers a Professional Welder program, as well as an Associate of Occupational Studies in Welding Technology degree.
Additional Sources
1. http://www.bls.gov/ooh/production/welders-cutters-solderers-and-brazers.htm#tab-2
This blog has been labeled as archived as it may no longer contain the most up-to-date data. For a list of all current blog posts, please visit our blog homepage at https://www.tws.edu/blog/